Night vision vs thermal
When it comes to enhancing visibility in low-light conditions, two technologies stand out: night vision and thermal. Both offer unique capabilities that can greatly impact your hunting, surveillance, or outdoor adventures. But how do they differ, and which one should you choose? In this article, we will explore the key differences between night vision and thermal scopes to help you make an informed decision and optimize your visibility in the dark.
Picture this…..
You are in a very dark room without any windows and can’t see a thing, then all of a sudden, the door to the room is opened. And immediately, because it’s bright outside, you are able to see everything that’s inside the room.
Here is what happened…
The light from outside was able to illuminate the room and all the objects inside. The light shone on the objects was then reflected into your eyes. And this provided you with clear well-defined images depicting the objects.
NIGHT VISION
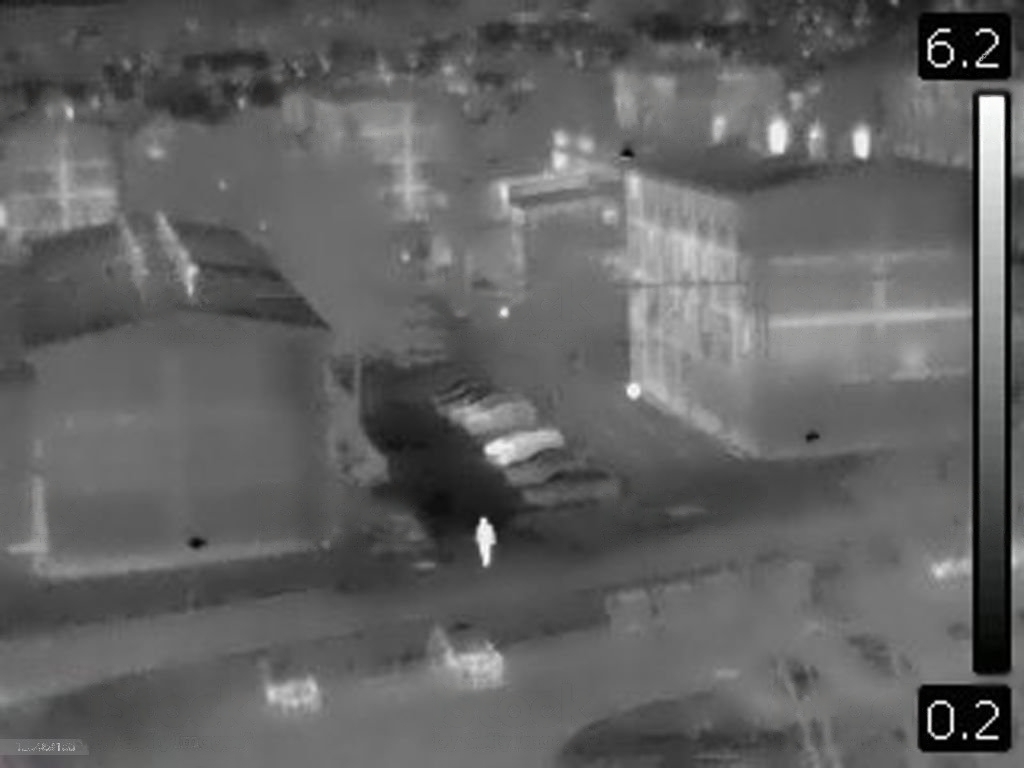

How Night Vision Works
Night vision devices function the same way as our eyes. This means that they need light to bounce off of objects into the lens for the device to make out the image of the object. This also means that if there isn’t any light, the night vision device is useless just like your eyes in that dark room.
so here is actually how night vision devices work….
A night vision device has an image intensifier inside that amplifies ambient lighting surrounding an object. Ambient light can be as little as light from a firefly, or the stars. Once this light bounces off the object and gets into the night vision device through the lens, it meets a photocathode. That transforms the photons that make up light into photoelectrons
The photoelectrons then strike a multi-cathode plate that exponentially multiplies them, before they can be converted back to photons. This whole process then results in a clearer image of the target object.
Night Vision During The Day
Since night vision magnifies even the smallest of lights, one can only imagine what it would do if exposed to a great deal of light. Using night vision devices during the day can be damaging to your eyes as well as the equipment itself. Because it was purposefully designed for low light conditions.
Nowadays, however, we have some devices that do not use the intensifier tubes with a photocathode, but rather rely on digital means of amplifying the ambient light. These devices can be used in daylight without suffering any damaging effects.
See also: Can you use night vision scope during the day.
Infrared Illuminator
It’s a confusing gadget to many because most people believe that night vision devices do not need any assistance to work in the dark. Matter of fact, they do.
Imagine the infrared illuminator as an invisible flashlight used the same way we use a normal LED flashlight to illuminate objects at night. Infrared has a higher wavelength than normal light that’s why it is not visible to the human eye. But it’s very visible through a night vision device.
The IR illuminates the target objects when there is no ambient light so that you are able to see an image. Just like you would use a flashlight in that dark room.
THERMAL IMAGING
Thermal imaging is a very different technology to the night vision, but it’s still able to give you images in the dark. The images however do not appear like normal images but a thermogram, where each color represents a particular temperature range.
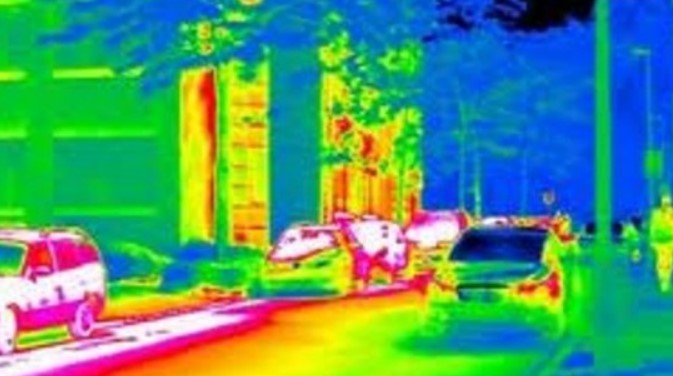
How Thermal Imaging Works
Unlike night vision which relies on the light reflected from an object to form an image, thermal imaging relies on heat. This means it will still function even when it is completely dark without any ambient light.
The thermal imagers use a thermal sensor known as a microbolometer. The microbolometer is made up of pixels each capable of detecting a specific range of temperature, and then displaying it in a different color. The sensor detects even the tiniest difference in heat, as low as 0.01°C between an object and its surroundings.
let us note that every object including ice emits some form of thermal energy to the surrounding. Additionally, because most animals are exothermic, a thermal imager can easily see the large amount of heat that they release.
It is evident that a block of ice won’t produce the same amount of heat that a buffalo would. As a result, the thermogram would show the ice and buffalo in distinct colors if they were placed side by side. Consequently, you will receive a defined image of the two objects.
Uses of Thermal Imagers
Because of their ability to work when it’s completely dark, and display a thermogram of targets hidden behind obstructions. The thermal imager has really proven useful in activities that include, hunting, search and rescue, law enforcement, and hiking. Modern thermal imagers are also lightweight and easy to use.
See also: The best thermal monocular for the money
Night Vision Vs Thermal Scopes
These two serve the same objective of allowing you to see images in low light or, in the case of a thermal scope, in complete darkness..
But it’s clear that the thermal imaging rifle scope has a few minor advantages over night vision.
Advantages of the thermal imager
- Don’t require ambient lighting to function
- Aren’t affected by too much light and will work well during the day
- Work in difficult circumstances like when it’s completely dark, in smoke, and in obstructions.
- Doesn’t require an additional illuminator when it’s pitch-dark.
CONCLUSION
The decision to utilize a thermal imager or a night vision gadget will ultimately depend on the user’s preferences and budget. Some users prefer the night vision gadget because it is less expensive and can be used in complete darkness when combined with an illuminator.
Others may employ the two devices in various combinations, such as utilizing one to locate the target and the other to shoot at it. Regardless of the decision, we believe that this article offers the most comprehensive review of the distinctions between the two types of devices.
Related posts:
